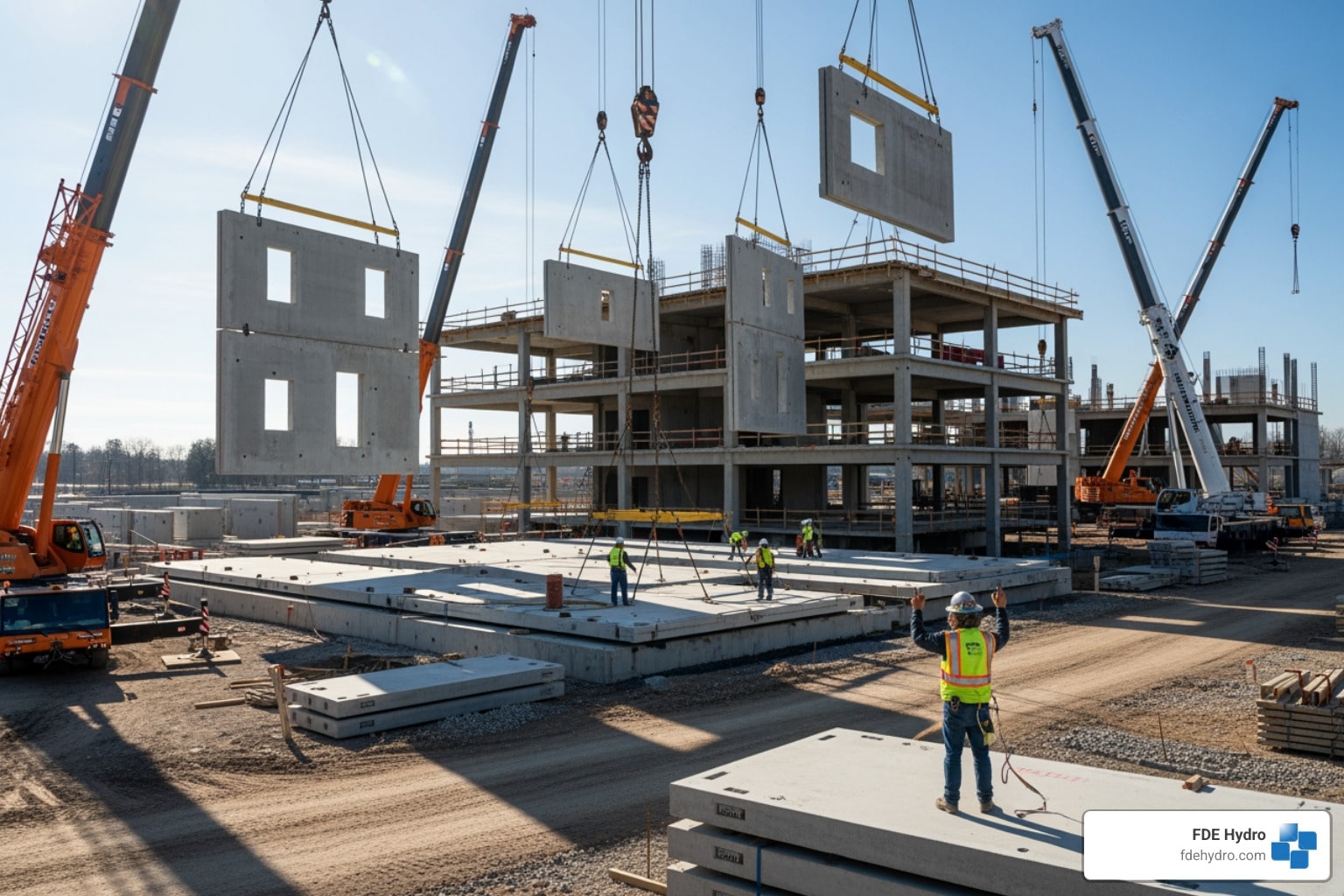
Why Modular Precast Concrete Matters for Modern Infrastructure
Modular precast concrete is a construction method where concrete elements are prefabricated in a factory and assembled on-site. This approach significantly reduces environmental impact, accelerates timelines, and increases productivity compared to traditional methods, making it critical for infrastructure like hydropower facilities and dams where reducing costs and timelines is paramount.
Key benefits of modular precast concrete:
- Speed – Up to 30% faster than poured-in-place construction, with modules installed in hours or days instead of weeks
- Quality – Factory-controlled manufacturing minimizes errors and enables use of high-performance materials
- Durability – Structures last 100-150+ years with superior resistance to fire, storms, floods, and earthquakes
- Sustainability – Reduces waste, enables material reuse, and can achieve 60% better energy efficiency
- Cost – Lower overall project costs through reduced labor, faster timelines, and less site disruption
The construction industry generates about 38% of global CO2 emissions. Traditional methods create significant waste and are prone to weather delays. In contrast, industrialized prefabrication optimizes material use, improves quality management, and dramatically reduces on-site construction time, offering a proven solution to the challenges of large-scale civil construction.
I’m Bill French Sr., Founder and CEO of FDE Hydro, and I’ve spent five decades in heavy civil construction, including groundbreaking work with modular precast concrete on projects like the I-93 Fast14 bridge construction. My experience has shown that this construction method represents the future of efficient, sustainable infrastructure development.
Modular precast concrete definitions:
The Core Principles: How It Works and Why It’s Different
Think of modular precast concrete as building with sophisticated, giant blocks instead of pouring concrete on-site. It’s a fundamental shift from traditional construction. Instead of dealing with weather, multiple crews, and material logistics on a chaotic site, we manufacture standardized concrete elements in a controlled factory environment. These precision-engineered pieces are then transported and assembled on-site like a puzzle.
Traditional construction is unpredictable. Rain, snow, or extreme heat can delay projects and affect quality. With modular precast concrete, we eliminate these variables. Manufacturing indoors ensures consistent quality and dramatically reduces waste. The accuracy of factory production means pieces fit together perfectly, a level of precision nearly impossible to achieve in the field.

The speed difference is remarkable, with projects completed months faster. For infrastructure like hydropower systems, this speed means faster delivery and lower costs. This approach also leads to cleaner, more organized sites with less noise and disruption. Modular Construction Techniques have transformed how we build critical infrastructure.
| Feature | Modular Precast Construction | Traditional On-Site Construction |
|---|---|---|
| Timeline | Rapid turnkey (weeks/months), up to 30% faster, weather-independent | Slower (months/years), susceptible to weather delays |
| Quality Control | Factory-controlled, integrated quality checks, minimized inaccuracies | On-site variability, weather-dependent, potential for human error |
| Waste Reduction | Optimized material flows, reduced on-site waste | Significant on-site waste generation, material inefficiencies |
| Weather Impact | Manufacturing unaffected by weather, indoor assembly | Highly susceptible to weather delays and conditions |
| Site Congestion | Minimized on-site labor, fewer trucks, less noise | High traffic, noise, and labor density on-site |
| Material Use | Enables high-performance, resource-efficient materials | Standard materials, often less optimized for performance |
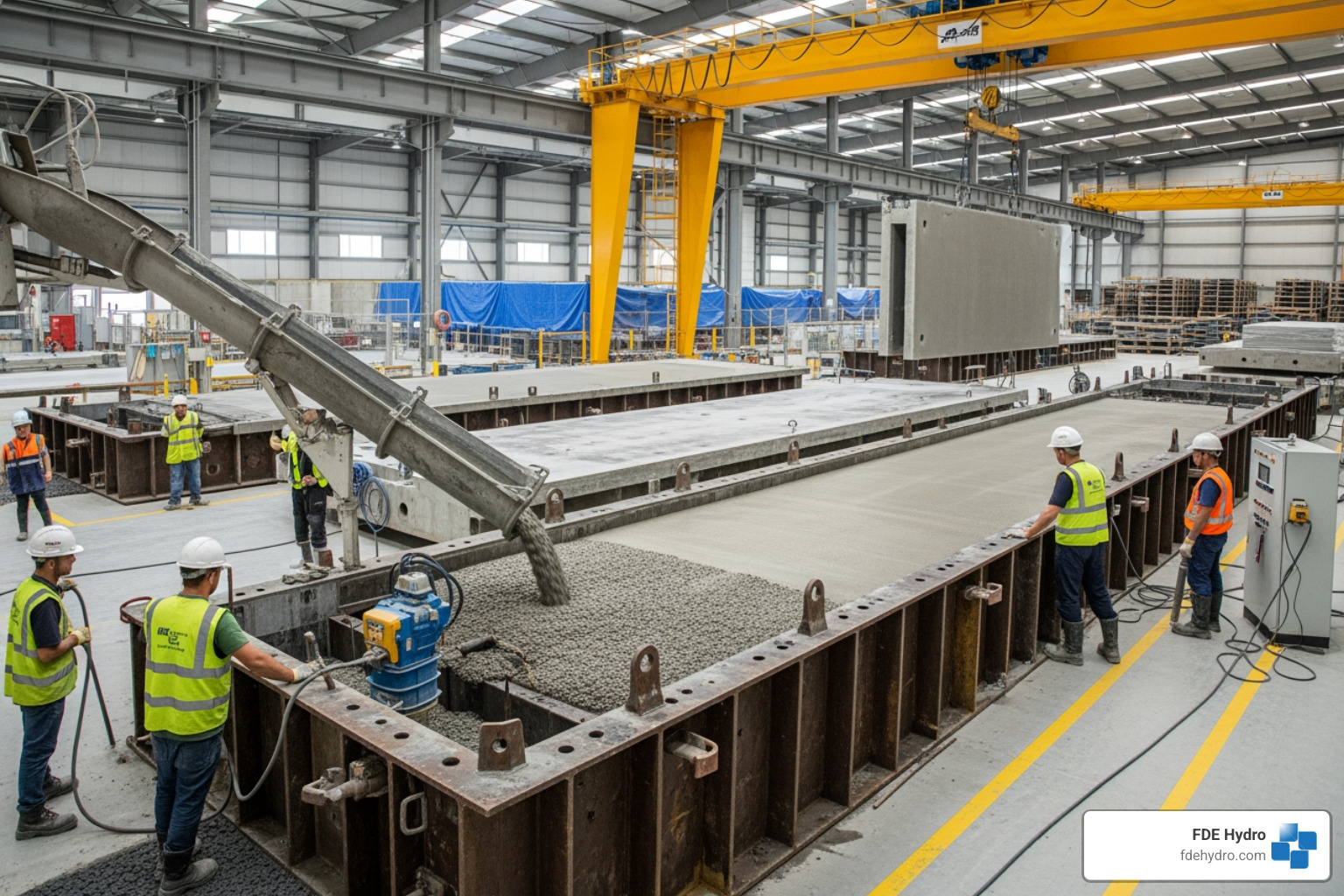
The Process of Modular Precast Concrete Manufacturing
Creating modular precast concrete elements is a precise, orchestrated process that begins long before on-site work.
It starts with design and engineering, where advanced software like Building Information Modeling (BIM) and Computer-Aided Design (CAD) are used to create inherently modular structures. Each element is engineered to the millimeter for strength, efficiency, and ease of assembly. These digital tools, which have evolved since the 1980s, enable mass customization with incredible precision.
Next, high-precision, often reusable molds are fabricated based on the designs. The concrete casting occurs in a controlled factory, allowing the use of high-performance mixes under ideal temperature and humidity. The curing process is also controlled, often accelerated with steam or heat to achieve strength rapidly and consistently. Finally, factory finishing (like insulation or waterproofing) is applied before modules are transported to the site, ready for installation.
From Factory to Footprint: On-Site Assembly
When modular precast concrete elements arrive, the project shifts into high gear. While modules are manufactured, site preparation like laying foundations occurs simultaneously. This just-in-sequence delivery minimizes site congestion, noise, and the number of vehicles compared to traditional construction.
Large cranes handle crane erection, lifting modules into place. Entire sections can be installed in a single day—work that would take weeks with poured-in-place methods. Specialized connection technology securely joins the modules, creating a monolithic structure. This process requires minimized on-site labor, resulting in a safer, more efficient site with less construction noise and congestion. This rapid, turnkey construction is a game-changer for delivering critical infrastructure like hydropower plants and water control systems quickly and efficiently.
The Evolution of Building: From Historical Concepts to Modern Systems
The concept of modular precast concrete is over a century old. Early experiments with precast elements appeared in the late 1800s, such as reinforced concrete beams in the 1891 Biarritz Casino and room-sized modules in 1896. By the early 20th century, architects like Walter Gropius championed prefabrication for affordable housing, and large-scale projects like Liverpool’s Eldon Street Mass Housing in 1905 proved its viability.
The real boom occurred after World War II, when Europe’s need for rapid rebuilding drove the “Mass Production and Standardization” era. Systems like I-464 and Camus used large, standardized precast panels. While fast, these “closed modular systems” resulted in monotonous designs and limited flexibility.
In response, the “Open Prefabrication Period” (1970-1985) introduced compatible components from various manufacturers, allowing for more creative freedom. This shifted the focus from monolithic modules to flexible component assembly.
The digital revolution, starting around 1985, transformed manufacturing. CAD (Computer-Aided Design) and PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) systems enabled mass customization, combining mass-production efficiency with custom-design flexibility. This dramatically reduced labor and increased precision.
By the 2000s, Building Information Modeling (BIM), combined with CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing), created a seamless digital workflow from concept to production. Today, we can design, simulate, and generate manufacturing instructions within a single integrated environment. This evolution is what makes modern modular precast concrete so capable, allowing us to build smarter and with higher quality than ever. Research on Modularisation in Construction and Precast Building Systems documents this journey.

Key Advantages of Modular Precast Concrete
After five decades in heavy civil construction, I’ve seen that modular precast concrete stands apart. It’s a reimagining of how we build critical infrastructure, offering transformative advantages in speed, durability, sustainability, cost, safety, and resilience. These are not abstract claims but measured outcomes on real projects, from hydropower facilities to water control systems.
Accelerated Construction Timelines
Time is money in construction, and traditional schedules are vulnerable to weather and labor issues. Modular precast concrete changes this equation, achieving up to 30% time savings compared to conventional methods.
The key is weather-independent manufacturing. While on-site work halts for rain or snow, our factories produce high-quality modules in climate-controlled facilities. When modules arrive on-site, components that would take weeks to build are installed in hours or days. This rapid turnkey approach, detailed in our work with Rapid Installment of Module Precast Civil Infrastructure, is invaluable for projects with tight seasonal windows, such as hydropower facilities.
Best Durability and Resilience
Infrastructure like dams and hydropower plants must last for centuries. Modular precast concrete delivers an extraordinary lifespan of 100 to 150 years or more, thanks to high-performance materials and factory-controlled quality that eliminates on-site inconsistencies.
Beyond longevity, these structures offer superior resistance to disasters like tornadoes, earthquakes, floods, and fires. This resilience comes from the inherent strength of engineered precast concrete. The structural integrity achieved in a factory simply cannot be matched in the field, where curing conditions are variable. This durability also means low maintenance requirements, leading to dramatically lower lifecycle costs and greater long-term confidence for project owners.
Sustainability and Economic Benefits
The construction industry is a major contributor to global environmental challenges, causing about 38% of global CO2 emissions and consuming 85% of mineral raw materials. Modular precast concrete offers a more sustainable path.
Factory production optimizes material flows, drastically reducing the waste common on traditional job sites. The resulting structures can also be up to 60% more energy-efficient due to superior insulation and airtight construction. Furthermore, the modular design supports a circular economy; modules can be reused, re-deployed, or recycled, minimizing demolition and extending material life.
These environmental advantages are complemented by economic benefits. Modular precast concrete typically costs less over the asset’s lifecycle due to reduced labor, faster completion, and lower maintenance. This value proposition, detailed in Why Precast Cost Less, makes renewable energy infrastructure more affordable and accessible.
Modern Applications and the Role of Technology
The versatility of modular precast concrete has expanded from simple structures to sophisticated, mission-critical infrastructure. At FDE Hydro, we apply these techniques to challenging water projects across North America, Brazil, and Europe, where cutting-edge technology is the foundation of our success.
Diverse Infrastructure Applications
Our work at FDE Hydro centers on replacing aging water infrastructure. We use our patented modular precast concrete technology to construct hydropower plants and retrofit dams with unprecedented speed and efficiency. This approach extends the life of critical community assets.
The impact of this technology spans multiple sectors:
- Bridge Construction: Rapid replacement systems allow entire bridge sections to be installed overnight, minimizing traffic disruption, as seen in A National Example of Rapid Bridge Construction Using Modular Precast Elements.
- Water Control Systems: Factory-made elements ensure reliability for everything from complex aqueducts to flood control structures.
- Tunnels: Precast segments create stable, low-maintenance underground passages.
- Retaining Walls: Precast systems manage difficult terrains and protect vital infrastructure.
Other applications include utility buildings, pump stations, and water treatment facilities, all benefiting from the precision of factory manufacturing. The Precast/Prestressed Concrete Institute showcases many such Modular Components from the Precast/Prestressed Concrete Institute, which serve as ready-to-install “building blocks.”
The Impact of Technology and Overcoming Challenges
Modern technology makes modular precast concrete exceptional. Building Information Modeling (BIM) is central, allowing us to create a complete virtual model to simulate construction and prevent conflicts. CAD/CAM systems bridge design and reality, translating precise digital plans into physical elements. Automation in manufacturing further improves accuracy, safety, and quality.
However, the method has considerations that require expertise. Transportation logistics for large modules demand careful planning and specialized equipment. Connection complexities require advanced engineering to ensure structural integrity, especially for dams. Perhaps most importantly, success depends on early design integration. The modular approach must be part of the project from its inception, requiring close collaboration between designers, engineers, and manufacturers.
These challenges are not roadblocks but factors that are managed through experience, planning, and innovation.
The Future of Construction: Trends and Innovations
The evolution of modular precast concrete is accelerating, driven by the global need for smarter, more sustainable infrastructure. Future trends promise to make this method even more powerful.
Mass customization is becoming standard. Digital design and automated manufacturing allow for unique, shape-optimized elements that meet specific project needs efficiently. This supports higher ecological standards and CO2 reduction by enabling precisely designed, high-quality components.
Breakthroughs in high-performance concrete are also emerging. New mixtures, including self-healing variants, ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC), and low-carbon concretes, are making modules stronger, more durable, and more sustainable. These materials allow for thinner, lighter, yet more robust structures.
We are also moving toward smart modules with integrated technology. Embedded sensors can monitor structural health, fiber optics can provide data, and integrated systems can manage heating and cooling. These intelligent modules will offer real-time performance insights and predictive maintenance capabilities.
Further automation in factories and on-site, using robotics and drones, will streamline logistics, boost safety, and reduce labor needs. As labor shortages persist, automation is a necessity for updating infrastructure affordably. These innovations are enabling larger and more complex projects, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible with precast. Learn more about how precast is expanding its capabilities.
Conclusion
As we’ve seen, modular precast concrete is more than a construction method—it’s a transformative approach to building vital infrastructure. From its historical roots to today’s digitally-powered systems, it consistently outperforms traditional methods.
The advantages are clear: accelerated timelines, superior durability and resilience for a 100-150+ year lifespan, and significant sustainability and economic benefits. For projects like hydropower plants, dams, and bridges across North America, Brazil, and Europe, modular precast concrete is proving its worth. The integration of modern technology, from BIM to automation, enables unparalleled precision and scale.
At FDE Hydro, we are proud to pioneer this innovation with our patented technology for hydroelectric dams and water control systems. This represents a fundamental shift in the construction paradigm—a smarter, faster, and stronger way to build. It’s how we future-proof our infrastructure, ensuring reliability and efficiency for generations to come.
Want to dive deeper into how we’re revolutionizing hydropower solutions with our advanced modular precast concrete technology? We invite you to explore further.
Learn more about advanced hydropower solutions


