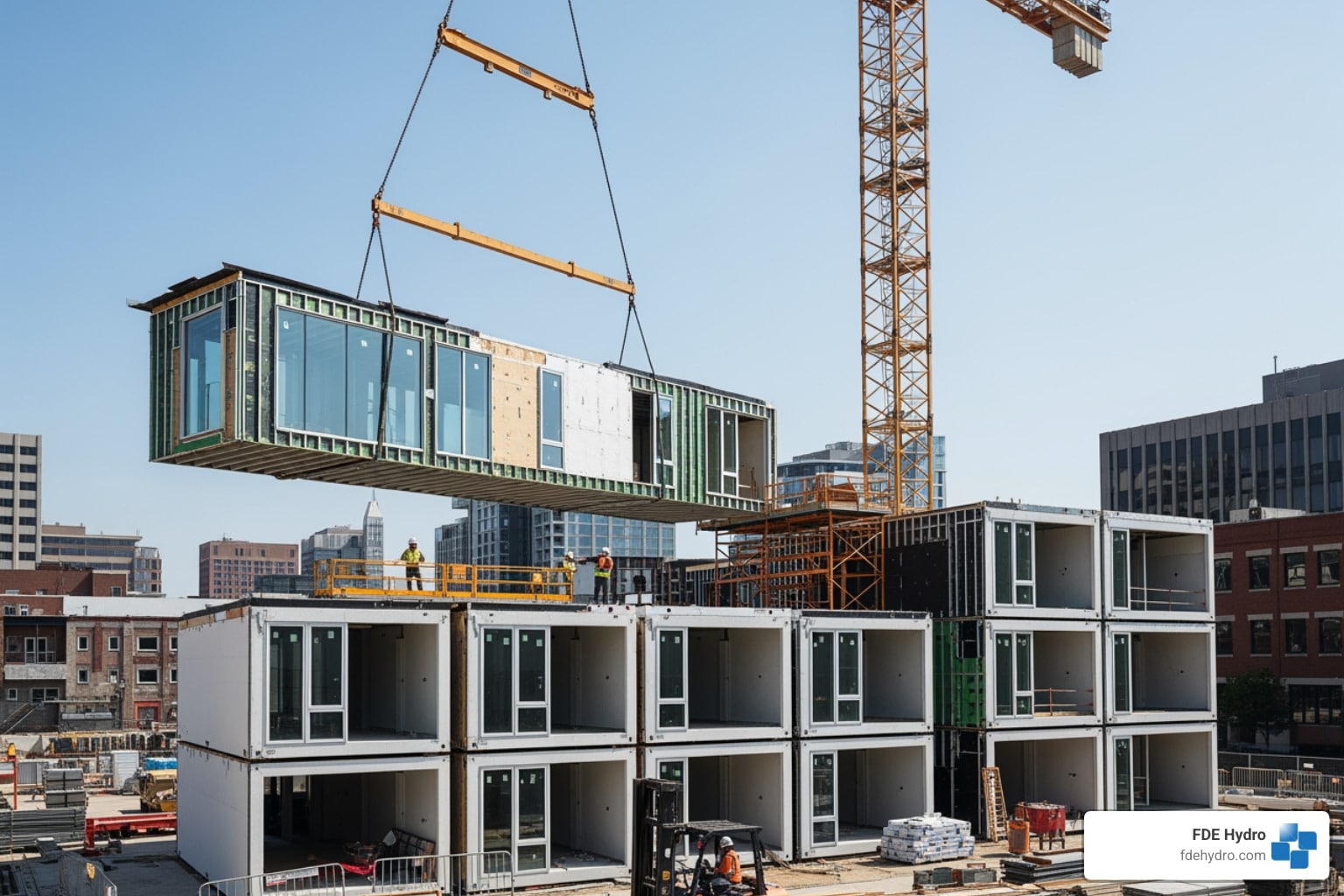
Why Innovative Construction Techniques Matter for Modern Infrastructure
Innovative construction techniques are changing how we build, offering faster project delivery, reduced costs, improved safety, and greater sustainability. Here’s what you need to know:
Key Innovative Construction Techniques:
- Prefabrication & Modular Construction – Building components off-site in controlled environments for rapid on-site assembly
- 3D Printing – Using additive manufacturing to create building components with minimal waste
- Robotics & Drones – Automating dangerous tasks and providing real-time site monitoring
- Augmented & Virtual Reality (AR/VR) – Visualizing designs and detecting clashes before construction begins
- Self-Healing Concrete – Using bacteria and healing agents to automatically repair cracks
- Green Building Materials – Incorporating recycled, renewable, and energy-efficient materials
Primary Benefits:
- 20-50% reduction in construction timelines
- Improved quality control through factory settings
- Improved worker safety by moving work off-site
- Lower environmental impact and material waste
- Significant long-term cost savings
The construction industry is at a turning point. Traditional methods struggle to meet the demands of modern projects—especially large-scale infrastructure like hydropower facilities, where time, cost, and risk are critical.
The good news? Technology and innovation are finally catching up. From modular construction that can cut foundation costs in half to cloud-based tools that 85% of contractors are already implementing, the industry is experiencing its most significant change in generations.
For project owners and decision-makers overseeing water infrastructure and hydropower development, these innovations aren’t just interesting—they’re essential. High capital costs, extended timelines, and operational uncertainties have long plagued conventional construction approaches. Modern techniques offer a path forward that reduces risk while accelerating delivery.
I’m Bill French Sr., founder and CEO of FDE Hydro, where we’ve spent the past decade pioneering modular precast solutions for the hydropower industry. Through my five decades leading major site and civil construction projects—from Boston’s Logan Airport to the I-93 Fast14 bridge project—I’ve witnessed how innovative construction techniques can transform project outcomes when applied correctly.
Related content about Innovative construction techniques:
The Rise of Off-Site Construction: Prefabrication and Modular Building
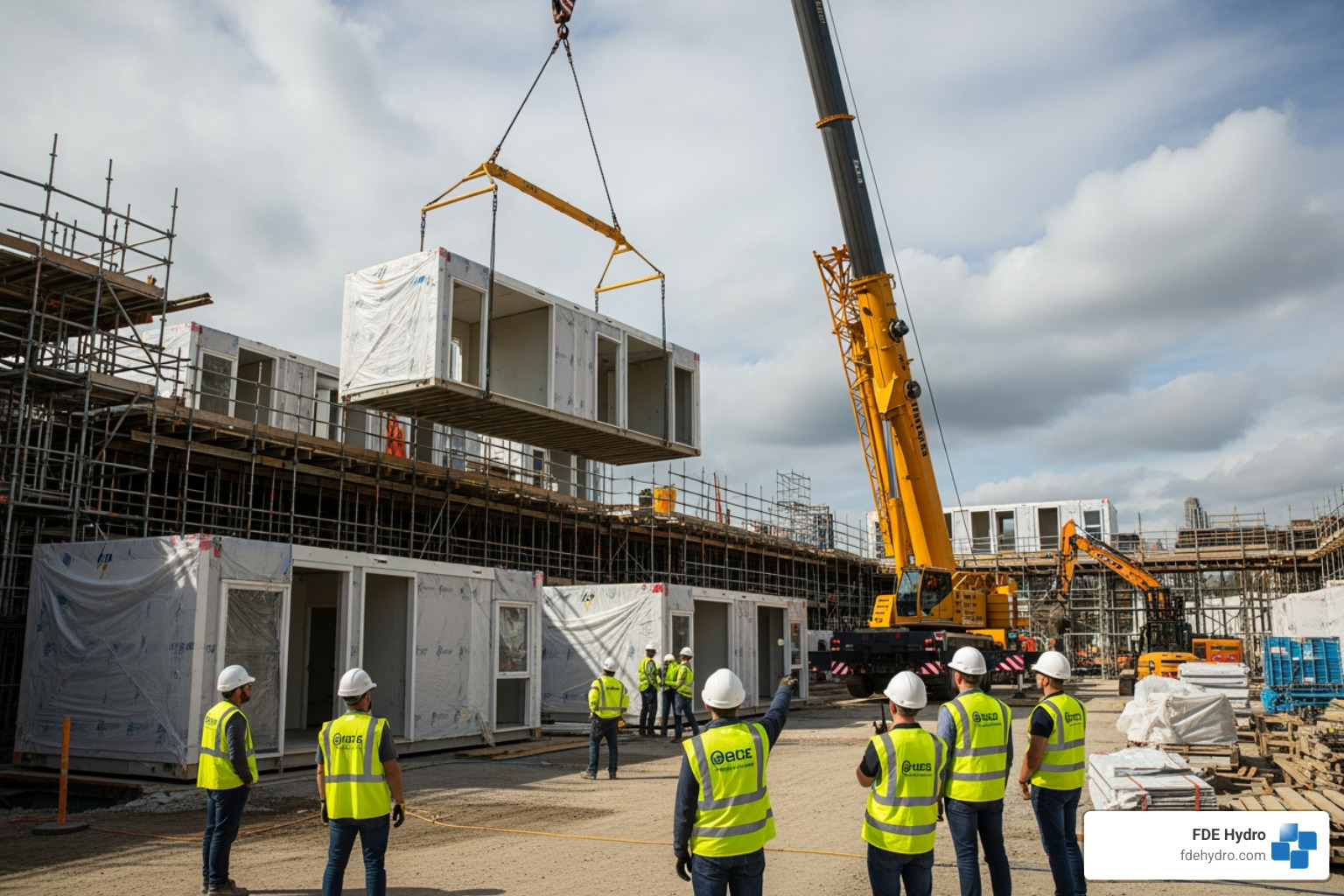

A significant shift in construction is the move towards off-site methods like prefabrication and modular building. Instead of building from scratch on-site, components and entire building sections are manufactured in controlled factory environments.
What is prefabrication? It’s the process of manufacturing building components, such as walls, floors, or roof trusses, in a factory and then transporting them to the construction site for assembly. Technology is making its benefits easier to access.
Modular construction takes this a step further. It involves creating complete, three-dimensional building sections or “modules” – sometimes even entire rooms like bathrooms or kitchens – in a factory. These finished units are then shipped to the site and assembled, much like stacking building blocks. This approach significantly reduces on-site labor and time. For instance, we’ve seen five laborers install hundreds of hospital bathrooms in days using modular construction.
The benefits of this factory-controlled environment are immense. It allows for rigorous quality control, ensuring that each component meets precise specifications before it even reaches the job site. This precision translates directly into higher quality and more durable structures. In fact, a Dodge Data & Analytics SmartMarket report indicates that 90% of contractors report improved productivity, quality, and schedule certainty when using prefabrication compared to traditional methods. It’s no wonder that 61% of contractors expect to employ prefabrication methods in at least 10% of their projects in the next three years, a significant increase from the 44% currently using it.
At FDE Hydro, we’re applying these very principles to critical water infrastructure projects. Our innovative modular precast concrete technology, often referred to as “French Dam” technology, allows us to build and retrofit hydroelectric dams and water control systems in North America, Brazil, and Europe with unprecedented speed and efficiency. By precasting large, complex components off-site, we minimize on-site work, reduce environmental impact, and deliver projects faster. You can learn more about our approach to Modular Construction Techniques, how we achieve Rapid Installment of Module Precast Civil Infrastructure, and view our various Precast Models.
How Prefabrication Improves Efficiency and Reduces Costs
The core appeal of prefabrication and modular construction lies in their ability to dramatically improve efficiency and slash costs. Let’s look at how:
| Metric | Traditional On-Site Construction | Modular Construction |
|---|---|---|
| Timeline | Longer, weather-dependent | Shorter, factory-controlled |
| Waste | Higher material waste | Minimized, recycled |
| Quality Control | Site-dependent, variable | Factory-controlled, consistent |
| Weather Delays | Frequent | Minimal |
The most striking benefit is schedule compression. Modular construction can lead to a remarkable 20–50% schedule compression. This speed is achieved because much of the work happens simultaneously: site preparation occurs while modules are being manufactured in the factory. This parallel processing eliminates many of the sequential delays inherent in traditional construction.
Reduced labor costs are another major advantage. With a significant portion of the work moved to a factory, the need for skilled labor on the job site is diminished, and tasks can often be completed more efficiently with specialized machinery. For instance, some foundation systems can cut the cost of creating a foundation in half compared to a traditional foundation. This is a game-changer, especially for projects with tight budgets.
Furthermore, off-site manufacturing inherently minimizes material waste. Factories are set up to optimize material usage, recycle scraps, and control inventory far more effectively than a busy, often chaotic, construction site. This not only saves money but also significantly reduces the environmental footprint of a project.
Our work at FDE Hydro exemplifies these advantages. Our modular precast solutions for infrastructure, such as those used in A National Example of Rapid Bridge Construction Using Modular Precast Elements and Modular Dam Construction, are designed to be fabricated off-site, allowing for quicker installation and substantial cost savings while maintaining superior quality and durability.
Digital and Robotic Innovations on the Modern Jobsite
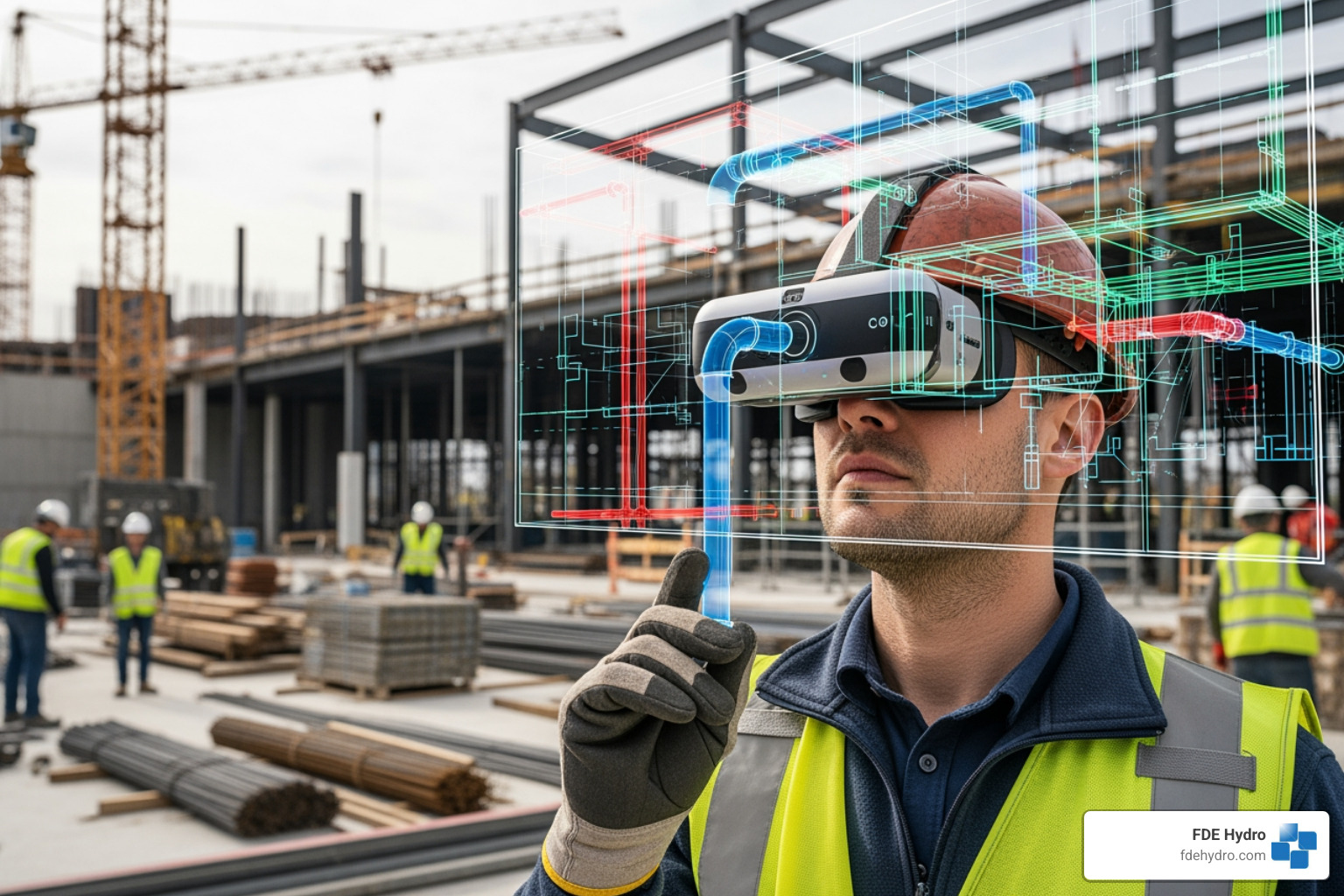

The digital revolution has certainly found its way to our construction sites, bringing with it a wave of innovative construction techniques that are redefining how we plan, execute, and monitor projects. This digital change, coupled with automation, empowers us to make data-driven decisions that improve every aspect of construction.
At the heart of this change is Building Information Modeling (BIM). BIM isn’t just about 3D models; it’s a collaborative process that allows architects, engineers, and contractors to work together on a detailed virtual representation of a structure. This helps us visualize and analyze design decisions, pinpoint interferences, and resolve errors before construction even begins, saving invaluable resources and preventing costly clashes.
Complementing BIM are cloud-based tools, which are proving to be the greatest efficiency driver in the market today. These systems connect workers to projects in real-time, providing a seamless flow of information between the back office and the field. This means real-time inputs of critical project data for analysis and response, improving collaboration and reducing project costs and durations. It’s no surprise that 85% of contractors have either implemented or are planning to implement cloud solutions. As research shows, cloud computing is an innovation enabler for other emerging construction technologies like BIM, IoT, virtual reality, augmented reality, and big data analytics. We believe that storing project data in the cloud is a no-brainer for any forward-thinking contractor.
3D Printing: Revolutionizing Speed and Material Use
When we talk about groundbreaking innovative construction techniques, 3D printing often comes to mind, and for good reason! This additive manufacturing process is literally building the future, layer by layer.
How does 3D printing work in construction? Large-scale 3D printers deposit successive layers of material, often a specialized concrete mix, to create building components or even entire structures. It’s fascinating to watch, and you can get a glimpse of the process in this video: What Is 3D Printing and How Does It Work? | Mashable Explains.
The benefits are compelling:
- Speed of construction: 3D-printed homes have been constructed in a matter of days in some regions. This speed is crucial for affordable housing projects, enabling quick and precise construction with minimal labor.
- Complex architectural designs: 3D printing allows for intricate designs and shapes that would be difficult, if not impossible, to achieve with traditional methods.
- Reduced material waste: By precisely depositing only the necessary material, 3D printing significantly minimizes waste, contributing to a more sustainable construction process.
The market for 3D printing in Architecture and Construction is projected to explode, reaching $47.95 million by 2030 (up from $10.94 million in 2021), indicating a staggering 101% CAGR growth rate. This signifies immense confidence in its potential.
However, it’s not without its challenges. We face regulatory problems and construction permits that are often designed for traditional methods, creating roadblocks for widespread adoption. Scalability is also a consideration – while impressive for individual homes, scaling up for large commercial or infrastructure projects is still an evolving area. According to 3drific, government regulations and construction permits are currently the biggest early roadblocks for 3D printed houses becoming widely available.
Drones and Robotics: Enhancing Safety and Productivity
The construction site of today is a far cry from what it was even a decade ago, thanks to the integration of drones and robotics. These aren’t just fancy gadgets; they are essential tools that are significantly enhancing safety and productivity.
Drones have become our eyes in the sky. They are invaluable for:
- Site surveying: Quickly capturing accurate topographical data.
- Aerial inspections: Reaching inaccessible areas for routine checks or damage assessment without putting workers at risk.
- Progress monitoring: Providing real-time aerial footage that helps project managers track progress and identify potential issues.
- Safety monitoring: Overseeing large sites to ensure compliance with safety protocols and respond quickly to incidents.
Meanwhile, robotics are taking on tasks that are repetitive, dangerous, or require extreme precision. Construction firms with a budget can apply robotics to any task that can be automated. This includes:
- Automated bricklaying: Robots can lay thousands of bricks per day with high precision.
- Demolition: Automating dangerous demolition tasks improves worker safety by keeping humans out of harm’s way.
- Welding and drilling: Robots perform these tasks with high accuracy and consistency, improving quality and reducing errors.
The primary benefits are clear: improved worker safety and increased productivity. While construction workers make up only 6% of the U.S. labor force, they account for 20% of worker deaths. Drones and robotics help mitigate these risks by automating hazardous tasks, allowing our human capital to focus on more important problem-solving. They can also operate 24/7, accelerating project timelines. This innovative approach aligns with our goal of Using Technology to Minimize the Duration of Impacts on our projects.
Augmented (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) in Construction
Imagine walking through a building before it’s even built, or seeing a digital blueprint overlaid onto a physical foundation as you work. This is no longer science fiction; it’s the reality of Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) in construction.
Virtual reality has become an integral part of the pre-construction process. It offers a low-stakes way to visualize an entire project, allowing us to:
- Design visualization: Immersive 3D models help clients and stakeholders truly understand the design.
- Clash detection: Identifying potential conflicts between different building systems (like plumbing and electrical) in a virtual environment, preventing costly rework on site.
- Stakeholder walkthroughs: Conducting virtual tours to gather feedback and make critical changes before any physical work begins, increasing efficiencies and preventing problems.
Augmented reality, on the other hand, transforms how workers interact with their tasks on-site. AR allows workers to overlay digital models onto physical sites, providing:
- Installation guidance: Workers can see exactly where components need to go, reducing errors and speeding up installation.
- Error reduction: By comparing the actual build to the digital model in real-time, deviations can be caught and corrected immediately.
- Task analysis: AR tools help workers analyze problems and assist with building and repair.
Technology leaders expect AR to surpass VR within the next 3 to 5 years, presenting a wide range of opportunities. When combined with Building Information Modeling (BIM), AR allows construction professionals to interact with a fully-rendered 3D model of a building before construction begins. These technologies are crucial for AI-Driven Development, enabling smarter design and more efficient execution.
Smart Materials and Sustainable Innovative Construction Techniques
Our commitment to building a better future extends beyond just speed and efficiency; it encompasses a profound responsibility towards sustainability. This is where smart materials and sustainable innovative construction techniques truly shine. The core principles of green building guide us towards energy efficiency, reduced carbon footprints, and ultimately, a more harmonious relationship with our planet. For us, particularly in water infrastructure, this means prioritizing Sustainable Infrastructure Development.
A prime example of successful sustainable construction is The Edge in Amsterdam, often hailed as the most sustainable office building in the world. This remarkable structure uses solar energy, rainwater harvesting systems, and intelligent lighting to achieve a near-zero energy footprint. Its success demonstrates the tangible benefits of integrating green building principles from concept to completion, including the often-overlooked aspect of IoT integration for smart, responsive building management.
Self-Healing Concrete for Increased Durability
Imagine concrete that can fix its own cracks. It sounds like something from a sci-fi movie, but self-healing concrete is becoming a reality, representing a truly innovative material. The concept, often referred to as bioconcrete, involves embedding bacteria or other healing agents within the concrete mix. When cracks appear and water seeps in, these agents are activated, producing limestone or other materials that fill the fissures. You can see this fascinating process in action here: What if cracks in concrete could fix themselves?.
The benefits of this material are substantial:
- Extended structural lifespan: By automatically repairing minor cracks, the concrete’s integrity is maintained, significantly prolonging the life of structures.
- Reduced maintenance costs: Less need for manual crack repair translates directly into lower long-term maintenance expenses.
- Increased durability: Structures become more resilient to environmental stressors and wear and tear.
While incredibly promising, challenges remain, primarily in terms of cost and ensuring the healing agents remain viable under various environmental conditions over extended periods. However, the potential for increasing the longevity of our infrastructure, including our hydropower facilities, is immense.
Green Building and Sustainable Materials
The pursuit of sustainability in construction is not a trend; it’s an imperative. Our core principles of green construction revolve around minimizing environmental impact throughout a building’s lifecycle, from material sourcing to operation and eventual deconstruction.
This involves:
- Use of recycled materials: Repurposing recyclables for construction began as early as the 1960s. Today, we incorporate materials like recycled steel, reclaimed wood, and even recycled plastics into new builds, significantly reducing the demand for virgin resources.
- Eco-friendly materials: We actively seek out eco-friendly materials that have a lower environmental footprint, such as bamboo (a rapidly renewable resource) and low-carbon concrete.
- Renewable resources: Modern timber frame construction is an excellent example. Using engineered wood products from sustainably managed forests reduces a building’s carbon footprint and offers a renewable alternative to traditional materials.
- Energy-efficient design: This includes integrating solar panels for renewable energy generation and implementing rainwater harvesting systems. Rainwater harvesting, for example, reduces reliance on municipal water supplies and mitigates stormwater runoff, which is particularly relevant to our focus on Sustainable Water Infrastructure. Passive solar design, optimizing window placement and using thermal mass materials, also minimizes the need for artificial heating and cooling.
These environmentally conscious choices help create greener buildings that are not only better for the planet but also offer long-term operational savings for owners.
The Advantages and Challenges of Adopting New Techniques
Embracing innovative construction techniques is a journey of weighing significant benefits against practical drawbacks. It’s a strategic decision that involves evaluating initial investments against long-term returns, understanding new skill requirements, and navigating the changing regulatory landscape. We believe the advantages far outweigh the challenges, especially for those committed to efficiency and sustainability.
Primary Advantages: Building Faster, Safer, and Smarter
The push for innovation is driven by a clear set of compelling advantages that fundamentally transform how we approach projects:
- Reduced construction time: Techniques like prefabrication, modular construction, 3D printing, and automation significantly cut down on project durations. Modular construction alone can achieve 20-50% schedule compression, turning months into weeks.
- Improved worker safety: Moving tasks from hazardous on-site conditions to controlled factory environments, and employing drones and robotics for dangerous jobs, drastically reduces risks. Between 1974 and 2007, the number of fatal injuries to employees in the UK fell by 73 percent and reported nonfatal injuries fell by 70 percent due to PPE regulations and technological advancements.
- Improved precision and quality: Factory-controlled environments and automated processes ensure higher accuracy and consistency, leading to superior quality structures with fewer defects.
- Cost savings: While some innovative methods might have higher upfront costs, they often lead to substantial long-term savings through quicker completion, reduced labor needs, minimized waste, and lower operational costs over the building’s lifespan. For example, some advanced foundation systems can cut foundation costs in half.
- Increased sustainability: From green building materials and energy-efficient designs to reduced material waste, these techniques promote environmentally responsible construction practices.
- Reduced material waste: Precision manufacturing and optimized processes in off-site construction minimize waste, contributing to both cost savings and environmental benefits.
Key Challenges to Widespread Implementation
Despite the overwhelming advantages, we acknowledge that the path to widespread adoption of innovative construction techniques is not without its problems:
- High initial investment costs: Implementing new technologies like large 3D printers, robotics, or advanced modular factories requires significant upfront capital. This can be a barrier for smaller firms or those with limited access to financing.
- Need for specialized training and skilled labor: These advanced techniques demand a workforce with new skills, from operating complex machinery and software to understanding digital workflows. There’s a current skills gap that needs to be addressed through training and education.
- Potential for job displacement: While new technologies create new types of jobs, there’s a concern that automation could displace some traditional construction roles, requiring a careful transition and retraining strategy for the workforce.
- Dependence on technology and power: Modern construction relies heavily on digital systems, power infrastructure, and connectivity. Any disruption in these areas can bring projects to a halt.
- Regulatory and building code problems: Existing building codes and regulations are often designed for traditional construction methods. Adapting these frameworks to accommodate rapid advancements in areas like 3D printing or new material compositions can be a slow and complex process, as seen with challenges in making 3D printed houses widely available due to government regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions about Innovative Construction Techniques
We often get asked about the practical implications of these new approaches. Here are some of the most common questions:
How do these innovative techniques specifically speed up construction projects?
The acceleration of construction projects through innovative construction techniques is multifaceted:
- Off-site manufacturing (modular/prefabrication): By building components or entire modules in a factory concurrently with on-site groundwork, we drastically reduce the overall project timeline. This parallel processing is a huge time-saver.
- Automation (robotics/3D printing): Robots can perform repetitive tasks much faster and with greater accuracy than human labor, while 3D printers can rapidly construct elements layer by layer.
- Parallel processing: As mentioned, tasks that used to be sequential can now happen at the same time, such as foundation work and module fabrication.
- Reduced weather delays: Factory-based work is immune to adverse weather conditions, ensuring consistent progress regardless of rain, snow, or extreme temperatures.
- Faster inspections (drones): Drones can conduct comprehensive site inspections and surveys in a fraction of the time it would take human inspectors, providing real-time data for quick decision-making.
- Improved planning (BIM/VR): Advanced digital tools like BIM and VR allow for meticulous planning and early clash detection, preventing costly delays and rework on-site.
Are modern construction techniques better for the environment?
Absolutely! Many modern innovative construction techniques are inherently designed with sustainability in mind, making them significantly better for the environment:
- Reduced on-site waste: Off-site manufacturing leads to precise material usage and efficient recycling programs, dramatically cutting down on landfill waste.
- Optimized material usage: Digital design and automated processes ensure that materials are used efficiently, minimizing excess and scraps.
- Use of sustainable and recycled materials: Green building practices actively incorporate renewable resources like timber, and recycled content, reducing the demand for virgin materials and their associated environmental impacts.
- Improved energy efficiency in finished buildings: Techniques like Insulated Concrete Forms (ICF) and passive solar design contribute to highly insulated, energy-efficient buildings, leading to lower operational energy consumption and reduced greenhouse gas emissions over the building’s lifespan.
- Lower carbon footprint over building lifecycle: From reduced transportation emissions due to fewer deliveries to more efficient energy use in the completed structure, the overall carbon footprint is significantly lowered.
What should future engineers consider when developing new construction techniques?
As we look ahead, engineers developing new innovative construction techniques must prioritize several key considerations:
- Sustainability and circular economy: Focus on materials that are renewable, recyclable, and have a low embodied carbon. Design for deconstruction and reuse.
- Cost-effectiveness and scalability: Innovations must not only be efficient but also economically viable and adaptable to projects of varying sizes and complexities, from small residential buildings to large-scale infrastructure like hydropower plants.
- Automation and AI integration: Continue to leverage AI and automation for greater efficiency, safety, and data-driven decision-making, including predictive analytics.
- Durability and low maintenance: Develop materials and methods that result in structures with longer lifespans and reduced maintenance requirements, like self-healing concrete.
- Human safety and collaboration: Ensure that new technologies improve, rather than compromise, worker safety and facilitate seamless collaboration among all project stakeholders.
The Future is Now: Embracing the Next Generation of Construction
The construction industry is at the cusp of a profound change, driven by a wave of innovative construction techniques that are reshaping every aspect of building. We’ve moved beyond merely constructing; we’re now designing, fabricating, and assembling with unprecedented precision, speed, and environmental consciousness. The shift towards a tech-integrated, sustainable industry is not a distant dream but a tangible reality that we are actively building today.
The future outlook includes increased automation, with robotics and drones taking on more complex tasks, and AI-driven project management, where algorithms optimize schedules, manage resources, and provide invaluable predictive analytics to mitigate risks before they arise. This intelligent approach allows us to make smarter decisions, faster.
At FDE Hydro, we are proud to be at the forefront of this evolution, playing a critical role in pioneering modular methods for essential civil infrastructure, particularly in hydropower and water control systems across North America, Brazil, and Europe. Our commitment to innovation is unwavering, as we strive to deliver projects that are not only efficient and cost-effective but also sustainable and resilient for generations to come.
As project owners and stakeholders, embracing these next-generation construction methods is no longer optional; it’s a strategic imperative for long-term success. We invite you to explore how these advancements can benefit your next project.
Learn how to mitigate risks for your long-term hydropower projects


