Why Advanced Manufacturing Matters for Modern Industry
Advanced manufacturing techniques represent the use of innovative technologies and processes—such as automation, artificial intelligence, robotics, and 3D printing—to improve efficiency, quality, and flexibility in production. Here’s what you need to know:
Key Differences from Traditional Manufacturing:
| Aspect | Traditional Manufacturing | Advanced Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Production Strategy | Mass production, standardized products | Customization, customer-focused |
| Labor Requirements | Semi-skilled workforce (3:1 ratio) | Highly skilled workforce (4:1 ratio) |
| Technology | Mechanized processes, manual oversight | Automation, AI, IoT, sensors |
| Investment Focus | Physical infrastructure and equipment | R&D and digital infrastructure |
| Flexibility | Dedicated production lines, limited adaptability | Dynamic, rapidly flexible systems |
| Data Usage | Manual tracking and reporting | Real-time monitoring and analytics |
Since the 1950s, these techniques have transformed how we build everything from aircraft components to medical implants. Manufacturing represents about 30% of energy use in the United States and supports nearly 13 million jobs—about 9% of the workforce. The adoption of automation and artificial intelligence has not only increased efficiency but has also led to higher precision and improved quality control.
The benefits are clear: companies can reduce production costs through lower labor expenses, cheaper materials, streamlined production lines, and reduced inventory. Advanced manufacturing techniques allow for improved competitiveness through improved outputs, increased value, better quality, and greater market responsiveness.
I’m Bill French Sr., Founder and CEO of FDE Hydro™, where we’ve applied advanced manufacturing techniques—specifically modular precast construction—to revolutionize hydropower infrastructure delivery. After five decades leading heavy civil construction projects, including landmark modular bridge work on the I-93 Fast14 project, I’ve seen how these innovations can transform traditional industries.
Handy Advanced manufacturing techniques terms:
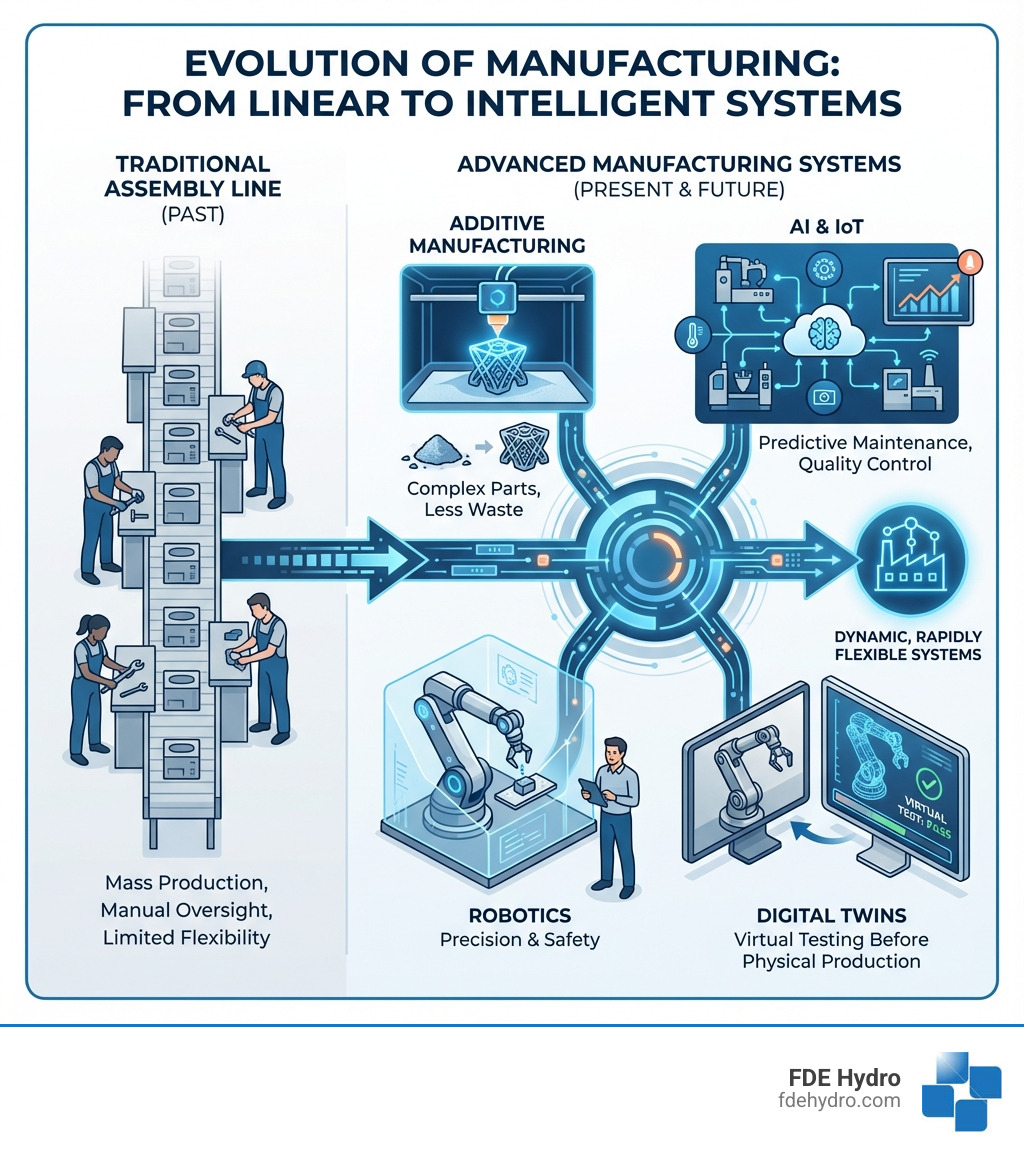
The Core Technologies Driving the Revolution
The manufacturing landscape is undergoing a profound change, driven by a suite of cutting-edge technologies that are reshaping how products are designed, produced, and delivered. These advanced manufacturing techniques are not just incremental improvements; they represent a paradigm shift towards smarter, more efficient, and more adaptable production systems.
At their heart, these innovations are powered by automation, sophisticated data analytics, pervasive interconnectivity, and intelligent smart systems. This convergence of technologies forms the backbone of what many call Industry 4.0, enabling manufacturers to achieve unprecedented levels of precision, customization, and responsiveness.
The goal is to create products of better quality, faster, and at lower costs, allowing companies to position themselves competitively in the market. We’re seeing this play out across various sectors, from the intricate world of aerospace to the robust demands of civil infrastructure. To dig deeper into how artificial intelligence is steering this evolution, you can explore our insights on AI-Driven Development.
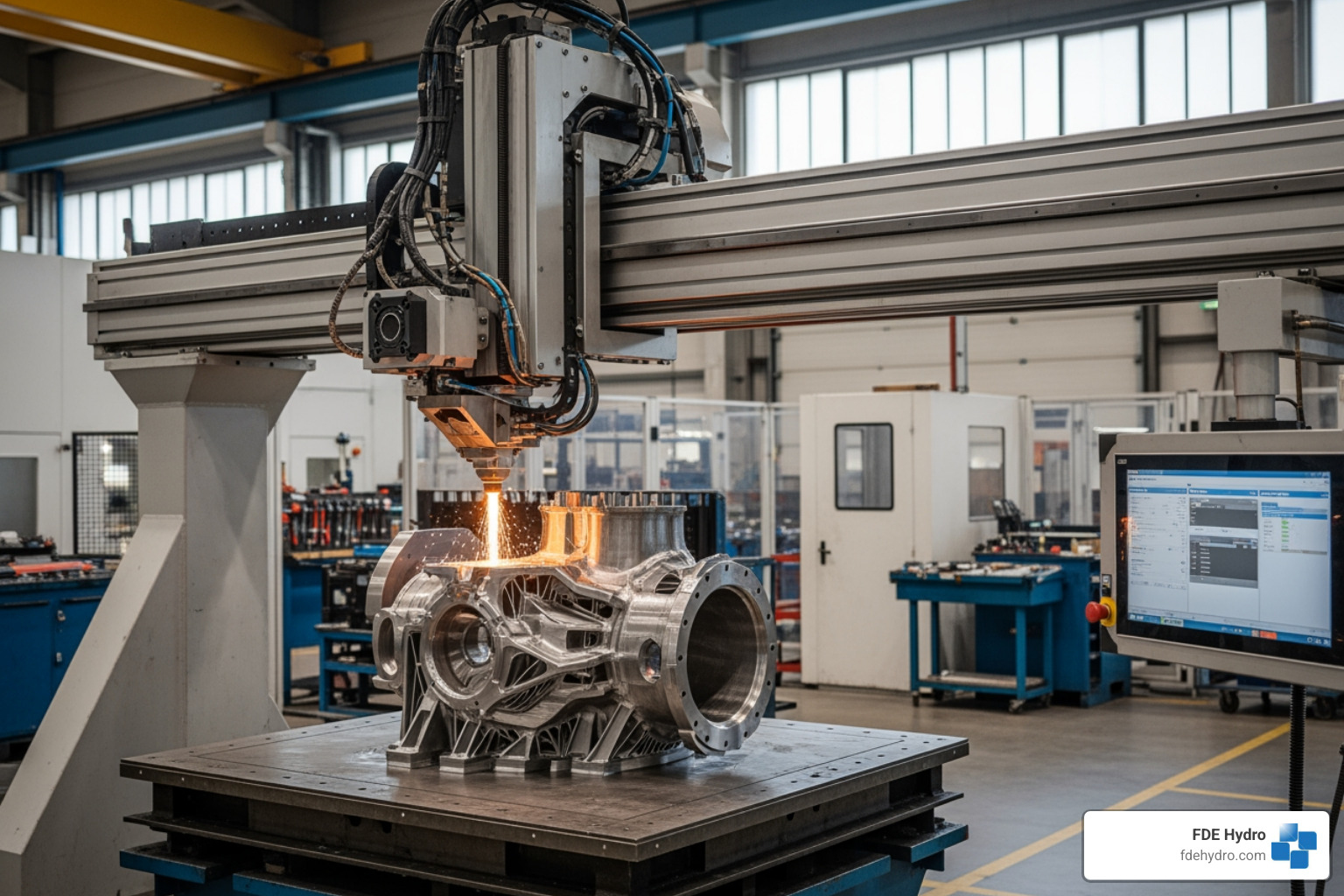

Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Perhaps one of the most visually striking and advanced manufacturing techniques is Additive Manufacturing (AM), commonly known as 3D printing. Unlike traditional “subtractive” methods that remove material to create a part, AM builds objects layer-by-layer from digital designs. This process allows for the creation of incredibly complex geometries that would be impossible or prohibitively expensive to produce with conventional methods. Think of it: a basic cube takes roughly the same time and effort to print as a highly intricate structure with the same enclosed volume. This concept of “complexity for free” is a game-changer.
AM significantly reduces material waste because it only uses the necessary material, making it a more environmentally friendly option. We’re talking about everything from metallic components for aerospace, plastic prototypes for consumer goods, to ceramic parts for specialized applications. This technology has progressed far beyond simple prototyping, now enabling the fabrication of functional end-use parts. For a comprehensive dive into this fascinating field, explore this review on Revolutionizing manufacturing: A comprehensive overview of additive manufacturing.
AI, IoT, and Big Data
In the field of advanced manufacturing techniques, intelligence is just as crucial as physical production. This is where Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and Big Data come into play, forming the nervous system and brain of modern factories. IoT involves embedding sensors, software, and other technologies into physical objects to connect and exchange data over the internet. These sensors collect vast amounts of data in real-time from machinery, production lines, and even environmental conditions.
This “Big Data” is then fed into AI systems that can analyze patterns, predict outcomes, and make intelligent decisions. For instance, AI algorithms can predict machine failures before they happen, enabling predictive maintenance and drastically reducing downtime. They can monitor product quality with incredible precision, ensuring consistent output and minimizing defects.
This real-time monitoring and data-driven decision-making empower manufacturers to optimize operations, improve efficiency, and respond rapidly to changes in demand or production issues. Our commitment to intelligent resource allocation is further detailed in our page on AI for Resource Management. Cloud computing plays a vital role here, enabling us to store, access, and process this data remotely, facilitating real-time communication and analysis across our facilities in the United States, Canada, Brazil, and Europe.
Advanced Robotics and Automation
Robotics and automation are the muscle and dexterity of advanced manufacturing techniques. Modern robots are no longer just caged machines performing repetitive tasks; they are becoming more intelligent, collaborative (cobots), and versatile. These advanced robots can handle precision tasks with superhuman accuracy and consistency, operate in hazardous environments without risk to human workers, and work 24/7 without breaks, significantly boosting productivity.
For example, automated CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) inspection ensures parts are made to the highest levels of quality and precision, a critical aspect in industries like medical devices or aerospace. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technologies, including Wire EDM, milling, turning, and grinding, allow for the machining of difficult-to-machine alloys to micro tolerances and high surface finishes.
This level of automation not only increases efficiency but also frees up human workers from mundane or dangerous tasks, allowing them to focus on more complex problem-solving, innovation, and oversight. As we’ve seen in our own work, these technologies are pivotal for ensuring successful project delivery on time, the first time.
Impact Across Industries: Benefits and Applications
The adoption of advanced manufacturing techniques is not merely about technological novelty; it’s about delivering tangible, transformative benefits that redefine competitiveness in the global market. We’re talking about a fundamental shift that leads to improved product quality, significantly reduced production costs, greater customization capabilities, and a faster time-to-market for new innovations.
These factors collectively improve a company’s competitiveness, allowing even smaller enterprises to stand toe-to-toe with industry giants. Our exploration into how these innovations are shaping the energy sector can be found on our Next-Gen Manufacturing: Energy Resource page.
Key Sectors Leading the Way
The revolution brought about by advanced manufacturing techniques is sweeping across numerous industries, with some sectors leading the charge due to their inherent demands for precision, innovation, and efficiency.
- Aerospace Industry: This sector relies heavily on AM for lightweight, complex components, robotics for precision assembly, and advanced materials for improved performance and fuel efficiency.
- Automotive Industry: From electric vehicle battery technology to lightweight chassis components and digital manufacturing processes, advanced manufacturing is driving innovation in car design and production.
- Medical Devices Industry: Custom implants, prosthetics, and intricate surgical instruments are being rapidly prototyped and produced with unparalleled accuracy using 3D printing and advanced robotics.
- Electronics Industry: The demand for smaller, faster, and more efficient chips and devices pushes the boundaries of nanotechnology, laser machining, and advanced materials.
- Energy Sector: Our own work at FDE Hydro™ is a prime example. We leverage modular precast concrete technology—an advanced manufacturing technique—to build and retrofit hydroelectric dams and water control systems in North America, Brazil, and Europe. This approach significantly reduces construction costs and time, echoing the broader trend of advanced manufacturing in developing cutting-edge, efficient, and environmentally friendly solutions like solar panels, wind turbines, and advanced batteries.
Industries utilizing advanced manufacturing techniques include:
- Automotive industry
- Aerospace industry
- Pharmaceutical industry
- Electronics industry
- Medical devices industry
- Robotics industry
- High-volume goods
- Rapid prototyping
Sustainability and Environmental Benefits
Beyond economic gains, advanced manufacturing techniques offer significant advantages in sustainability and environmental stewardship. This is a critical area where innovation can truly make a difference for our planet.
- Reduced Energy Consumption: By optimizing processes and using more efficient machinery, advanced manufacturing concepts help reduce the overall energy footprint of production. Powering manufacturing with renewable energy sources is also a growing trend.
- Less Material Waste: Techniques like additive manufacturing (3D printing) minimize waste by using only the material needed, unlike traditional subtractive methods. This is particularly impactful when working with expensive or rare materials.
- Recyclable Materials and Green Supply Chains: The development of novel materials, such as thermoplastic resins for recyclable wind turbine blades, and bio-optimized technologies for plastic waste recycling and upcycling, are direct outcomes of advanced manufacturing research. Furthermore, supply chain analyses help improve product life cycles, promoting greener practices from design to end-of-life.
- Greenhouse Gas Emission Reduction: The cumulative effect of these efficiencies and material innovations is a substantial reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. For those interested in how AI specifically contributes to these efforts, we encourage you to visit our AI for Sustainability page. The National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) has highlighted how advanced manufacturing focuses on energy efficiency, renewable energy integration, and product recyclability. You can learn more about this on their Advanced Manufacturing Energy Basics page.
A Practical Guide to Adopting Advanced Manufacturing Techniques
For any company, whether a large corporation or a small to medium-sized enterprise (SME), embracing advanced manufacturing techniques requires careful strategic planning. It’s not just about buying new machines; it’s about changing processes, upskilling your workforce, and often, rethinking your entire business model. The journey involves understanding the potential return on investment (ROI) and navigating various implementation barriers.
SMEs, in particular, might feel daunted by the initial investment and complexity. However, advanced manufacturing can level the playing field, allowing smaller companies to compete effectively by optimizing resource usage and reducing error rates. Low-cost, easy-to-implement technologies can offer significant productivity increases. For instance, America’s Seed Fund (SBIR/STTR) supports startups and small businesses in translating research into products and services, including advanced manufacturing. You can find more information on America’s Seed Fund for advanced manufacturing.
Here’s a comparison of key considerations for SMEs versus large enterprises:
| Consideration | SMEs | Large Enterprises |
|---|---|---|
| Investment | Phased, targeted, leverage grants/partnerships | Significant, strategic, R&D budgets |
| Skills | Upskilling existing staff, external training | Internal training academies, specialized hires |
| Scalability | Modular adoption, focus on specific needs | Enterprise-wide integration, global rollout |
| Risk | Higher perceived risk, focus on quick wins | Managed risk, long-term strategic view |
| Flexibility | Agile adaptation, rapid implementation | Complex integration, change management crucial |
Key Implementation Considerations
Successfully adopting advanced manufacturing techniques hinges on addressing several critical factors:
- Workforce Skills Gap and Technical Training: The shift from traditional to advanced manufacturing demands a highly skilled workforce. We need technicians proficient in data analytics, robotics programming, AI oversight, and sophisticated software. Companies must invest in technical training, reskilling, and upskilling programs for their existing employees, and collaborate with educational institutions to cultivate the next generation of talent.
- Initial Investment: While the long-term benefits are substantial, the upfront cost of advanced machinery, software, and infrastructure can be significant. Careful financial planning, exploring government grants (like those from the NSF in the US or similar programs in Canada and Europe), and understanding the ROI are crucial.
- Digital Infrastructure: A robust digital backbone is essential. This includes high-speed internet, secure networks, and cloud computing capabilities to support data exchange, real-time monitoring, and remote operations across facilities in places like New York, California, Kansas, or Brazil.
- Cybersecurity: As manufacturing becomes more interconnected, the risk of cyber threats increases. Protecting sensitive data, intellectual property, and operational systems is paramount. Implementing strong cybersecurity protocols is not just a technical necessity but also a way to boost competitive advantage by assuring clients of data safety.
The Role of Modular and Precast Methods
In our experience at FDE Hydro™, particularly in civil infrastructure, modular and precast methods stand out as highly effective advanced manufacturing techniques. These approaches embody many of the core principles of advanced manufacturing:
- Off-site Fabrication: Components, like our modular precast concrete elements for dams, are manufactured in a controlled factory environment. This allows for superior quality control, precise material mixing, and optimized production processes that are simply not achievable on a dynamic construction site.
- Quality Control: The factory setting enables rigorous testing and inspection, ensuring that every component meets the highest standards before it even leaves the plant. This translates to a more reliable and durable end product.
- Reduced On-site Labor: By pre-manufacturing large sections off-site, the amount of labor required at the construction location is significantly reduced. This not only lowers costs but also improves safety and minimizes disruption to the surrounding environment.
- Faster Installation: Modular components can be rapidly assembled on-site, dramatically cutting down construction timelines. We’ve seen this in our work on hydropower projects, where rapid deployment is a major advantage.
- For a deeper understanding of these methods, you can explore our page on Modular Construction Techniques and specifically Precast Concrete Technology. These techniques are a testament to how advanced manufacturing principles can be applied to large-scale, complex projects, yielding efficiencies and quality that traditional methods cannot match.
Frequently Asked Questions about Advanced Manufacturing
We often get asked about the nuances of advanced manufacturing techniques. Here, we aim to clarify some common queries.
What is the difference between smart manufacturing and advanced manufacturing?
While often used interchangeably, it’s helpful to think of smart manufacturing as a subset of advanced manufacturing techniques. Advanced manufacturing is a broader term encompassing all innovative technologies and methods that improve productivity, efficiency, and competitiveness in manufacturing. This includes everything from new materials and processes to automation and digitalization.
Smart manufacturing, on the other hand, specifically focuses on data-driven, automated processes and interconnected systems. It’s characterized by the extensive use of IoT, AI, and big data to create intelligent, self-optimizing factories. So, while all smart manufacturing is advanced, not all advanced manufacturing necessarily falls under the “smart” umbrella (e.g., a novel material development might be advanced but not inherently “smart” in its production without interconnected systems).
How does cloud computing improve advanced manufacturing?
Cloud computing is a game-changer for advanced manufacturing techniques because it enables companies to store, access, and process vast amounts of data remotely. This offers several key benefits:
- Scalability: Manufacturers can easily scale their computing resources up or down as needed, without investing in expensive on-premise hardware.
- Collaboration: Cloud platforms facilitate real-time collaboration among design teams, production engineers, and supply chain partners, regardless of their geographical location (e.g., between our offices in New York and our project sites in Brazil).
- Centralized Data Management: It provides a centralized repository for all manufacturing data, from CAD designs and production parameters to quality control reports. This single source of truth streamlines operations and reduces errors.
- Real-time Analysis: With data residing in the cloud, AI and analytics tools can process it in real-time, providing immediate insights for predictive maintenance, quality control, and operational optimization.
Essentially, cloud computing provides the flexible, powerful, and secure infrastructure needed to support the data-intensive nature of modern advanced manufacturing techniques.
What are digital twins and how are they used?
A digital twin is a virtual replica of a physical asset, process, or system. In the context of advanced manufacturing techniques, it’s like having a living, breathing digital copy of your factory floor, a specific machine, or even a product.
These digital twins are built using real-time data from IoT sensors, AI models, and sophisticated simulation software. They are used for:
- System Simulation: Engineers can run simulations on the digital twin to test new layouts, optimize production workflows, or predict the impact of changes without disrupting actual production.
- Process Optimization: By analyzing how the digital twin performs under various conditions, manufacturers can identify bottlenecks, improve efficiency, and fine-tune processes.
- Predictive Analysis: The digital twin can predict potential issues or failures in its physical counterpart, enabling proactive maintenance and preventing costly downtime.
- Reduced Physical Prototyping: Instead of building multiple physical prototypes, designers can test and refine product designs virtually using the digital twin, saving time and resources.
Digital twins provide a powerful tool for understanding, predicting, and optimizing complex manufacturing operations, making them an indispensable part of advanced manufacturing techniques.
Conclusion: Building the Future of Industry
We’ve journeyed through the intricate world of advanced manufacturing techniques, exploring how they are fundamentally reshaping industries across the globe. From the precision of additive manufacturing to the intelligence of AI and IoT, and the efficiency of advanced robotics, these innovations offer a compelling vision for the future of production. The benefits are clear: superior product quality, reduced costs, improved customization, faster time-to-market, and a significant boost in competitiveness. Crucially, these techniques also pave the way for a more sustainable future, minimizing waste and optimizing energy use.
For companies like ours, operating in vital sectors such as renewable energy and hydropower, embracing these techniques isn’t just an option—it’s a necessity. At FDE Hydro™, we are proud to be at the forefront of this revolution, particularly through our innovative modular precast concrete technology. This approach embodies the spirit of advanced manufacturing techniques by bringing factory-controlled precision, efficiency, and speed to the construction of hydroelectric dams and water control systems in North America, Brazil, and Europe. Our experience demonstrates that by leveraging these advancements, we can overcome traditional challenges, reduce construction time and costs, and deliver infrastructure that is both high-quality and sustainable.
The future of industry is dynamic, intelligent, and interconnected. By continuing to invest in research, foster skilled workforces, and adopt these transformative technologies, we are not just building products; we are building a better, more efficient, and more sustainable world.
To learn more about how we are innovating in the hydropower sector, we invite you to explore our work on Learn more about innovations in hydropower.


